Geographic Information System (GIS)
- The first GIS was created by Dr. Roger Tomlinson and then introduced in the early 1960 in canada.
- GIS is a computer-based information system which attempts to capture, store, manipulate, analyse and display spatially referenced and associated attribute data for solving complex research, planning and management problems.
- GIS is a system of hardware, software, data, and people organizing, collecting, storing, analyzing and disseminating information about the areas of the earth.
- GIS is an information technology which stores, analyses and displays both spatial and non-spatial data.
- GIS are specialized data bases that preserve locational identities of the information that they record.
GIS = Geographic+ Information + System
Geographic
Geographic ⇒ Spatially + referenced (geo-reference) data acquisition
Geographic: Relates to the places on the earth’s surface
- Where is something
- What is at a given location
Information system
Information system ⇒ software +hardware + database integrates, store, edits, analyzes, share and displays geographic information’s.
Information system: Manipulate, summarize, query, edit, visualize -work with information stored in computer database
GIS can transform data in to information.
DATA ⇒ COMPUTER ⇒ GIS ⇒ INFORMATION
Uses of GIS
GIS used for
- Transportation
- Hydrology
- Geology
- Crime
- Health
- Demographics
Components of GIS
1. Hardware
- Hardware is the computer on which a GIS operates.
2. Software’s
– GIS software’s provides the functions and tools needed to store, analyze, and display geographic information.
3. Data
- Possibly the most important component of a GIS is the data.
- Geographic data and related tabular data can be collected in house or purchased from a commercial data provider.
4. People
- GIS technology is limited without the people who manage the system and develop plans for applying it to real-world problems.
- GIS user range from technical specialist who design and maintain the system to those who use it to help them perform their everyday work.
5. Methods
- A successful GIS operates according to a well-designed plan and business rules, which are the models and operating practices unique to each organization.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
- GPS (NAVSTAR) is a satellite based navigation system that provides accurate positioning on the basis of constellation of 24 satellites and navigational facilities to the users.
- Initially GPS was designed for military use for US Department of Defense to give positioning information at any weather conditions and anywhere on the surface portion of earth. Later it was made available for civilians use also.
- GPS measures distance using the travel time of radio signals.
- Operated by: DOD(US Department of Defense).
- GPS is also known as the NAVSTAR (Navigation System with Time And Ranging).
- Number of satellites required for exact location: 4
- For precise measurement at least 3 satellites are required for 2D location of a point & 4 satellites are required for 4D location of a point.
Some Important Points About NAVSTAR
- NAVSTAR = Navigation System with Time And Ranging.
- Operated by US departed of defense.
- Accuracy for civilian user = ±100 meter.
- Accuracy for Military user = ±10 meter.
- Speed of Satellite = 3.9km/sec.
- 9 Satellite are in stand by.
- Height of Satellite = 11500mile.
- Total 6 orbit ( 4 Satellite in one orbit)
Different GPS systems available are
- NAVSTAR (Navigation System with Time And Ranging)
- GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
- GALILEO
- BEIDOU
- QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System)
- IRNSS (Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System ) (NAVIC)
Comparison of Global Navigation Satellite Systems of the World
NAME | Country | No of Satellites | Global/ Regional |
| NAVSTAR | U.S | 24 | Global |
| GLONASS | Russia | 24 | Global |
| GALILEO | Europe | 27 | Global |
| BEIDOU | China | 35 | Global |
| QZSS | Japan | 3 | Regional |
| IRNSS | India | 4 | Regional |
Remote Sensing
- Remote sensing is an art and science of obtaining information about an object or feature without physically coming in contact with that object or feature.
- Thus, remote sensing is the process of inferring surface parameters from measurements of the electromagnetic radiation (EMR) from the Earth’s surface.
- This EMR can either be reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface.
- Remote sensing is detecting and measuring electromagnetic (EM) energy emanating or reflected from distant objects made of various materials, so that we can identify and categorize these objects by class or type, substance and spatial distribution.
Principles of Remote Sensing
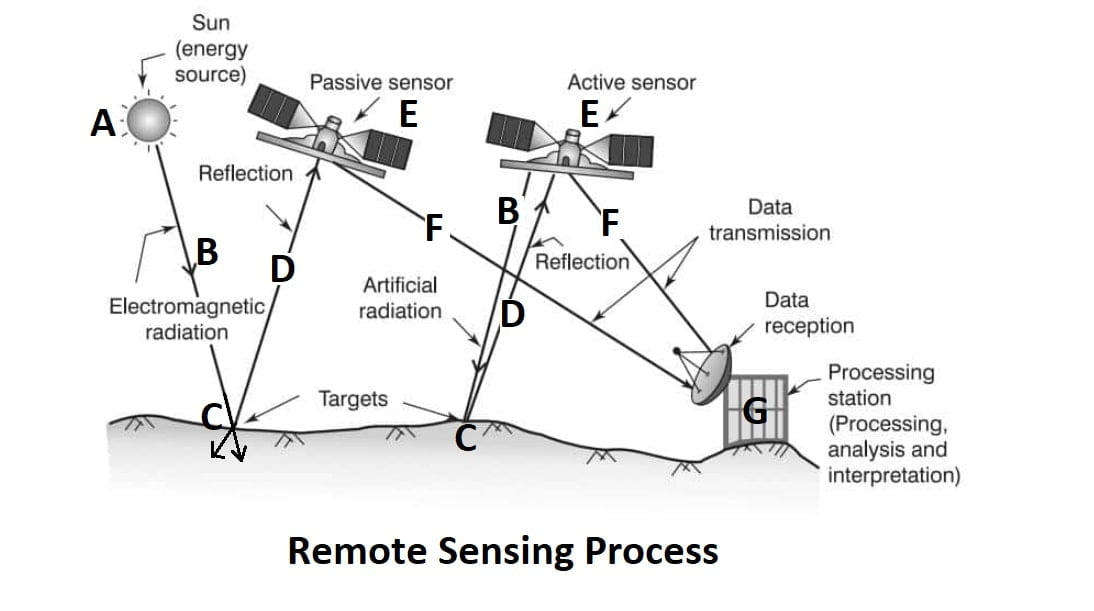
- Emission of electromagnetic radiation(SUN).
- Transmission of energy from the source to the object (Absorption and scattering of the EMR while transmission)
- Interaction of EMR with the object and subsequent reflection and emission.
- Transmission of energy from the object to the sensor.
- Recording of energy by the sensor (Photographic or non photographic sensors).
- Transmission of the recorded information to the ground station.
- Processing of the data into digital or hard copy image.
- Analysis of data
Remote Sensing Sensor Systems
The instruments for recording electromagnetic radiations are called sensors. The sensor systems are required to be placed on suitable observation platforms, which can be lifted to a predefined altitude. These may be tripod for field observation, aircraft and satellites. The aircrafts are mainly used for surveys of local or limited areas, whereas for a synoptic view of a large area, satellites are more useful.
Type of Remote Sensing Sensor Systems
- Active System
- Passive System
1.Active System
A system which utilizes man-made sources of energy for data collection is called an active system, e.g., taking photographs in dark places with the help of a flash bulb. The other examples of active systems are radar and laser scanner.
2.Passive System
A system that uses an existing source of energy, e.g., sun rays is called a passive system, such as taking photographs with a camera on a clear bright day.
NOTE: India have IRS (Indian Remote Sensing Satellite) named as IRs-1A,1B,1C,1D,P5,P7,P6. All these satellite low orbit satellite.