Formation of Soil
The process of formation of soil is termed as PEDOGENESIS. Soil is formed due to the weathering (erosion /wear and tear) of rocks. Weathering of rock can occur either physically or chemically.
Physical Process
- Impact and grinding of water.
- Impact and grinding of air/wind.
- Impact and grinding of ice.
- Splitting action of ice Gravitational force.
- Plant and animal.
Chemical Process
- Oxidation. (Reaction with oxygen, Reaction in the presence of oxygen. The process of removal of hydrogen is termed as oxidation.)
- Reduction. (Reaction in absence of oxygen. The process of removal of oxygen is termed reduction, and The process of adding hydrogen is termed reduction. )
- Carbonation. Reaction with carbon dioxide is termed carbonation. )
- Hydration. (Reaction with water is termed hydration)
- Leaching by organic acids and water.
Note: Leaching is the process of extracting a substance from a solid material that is dissolved in a liquid.
If soil is formed by physical weathering there is no change in mineral content of soil but if it is formed by chemical weathering mineral content of soil differs from that of rock.
- If the weathered material retains over the parent rock, it is termed Residual soil and If it is transported, it is termed Transportation soil.
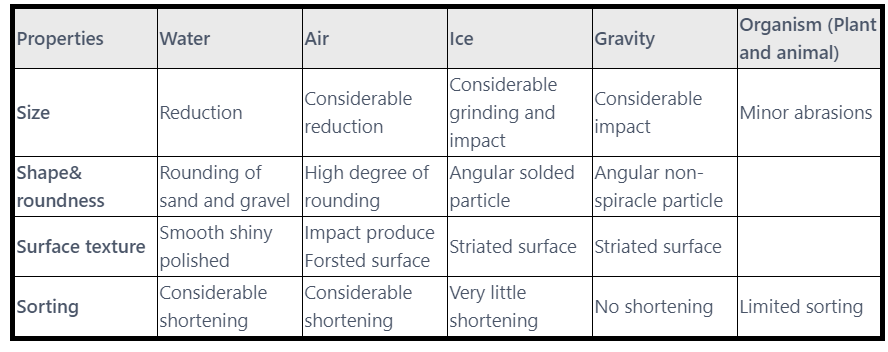
- The characteristic of soil: Size of particles, Shape and roundness, Surface texture, and Degree of shortness, depended upon the mode agency of transportation.
Mode of Transportation Effect on Characteristics of the Soil
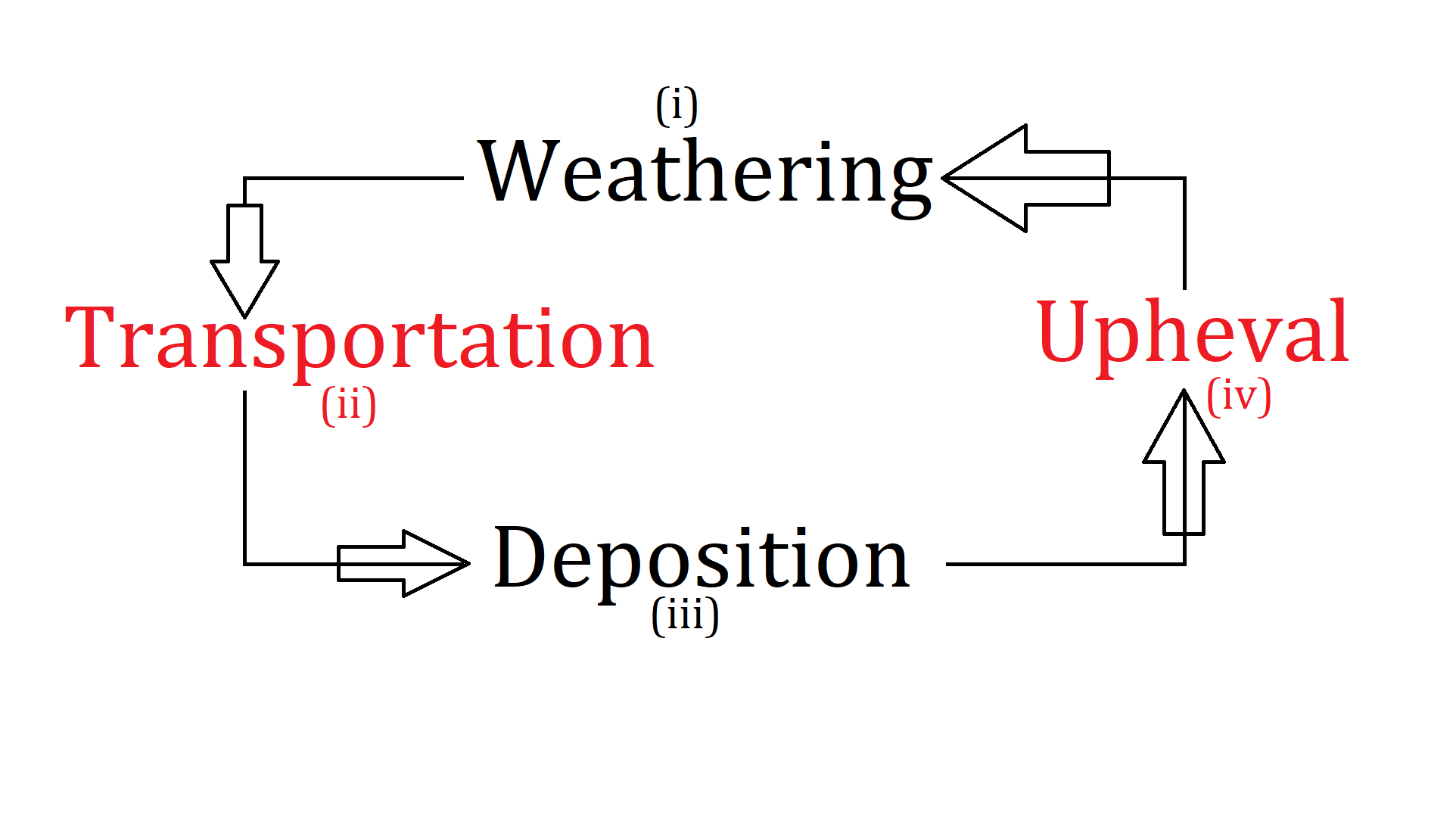
General Cycle Involved in Formation of Soil
- Weathering
- Transportation
- Deposition
- Upheaval
Weathering: Erosion /wear and tear.
Transportation: Carrying from one place to another by any agency (Water, air, ice, gravity, organism).
Deposition: Retain transportation.
Upheaval: Increase in the level of the ground is termed upheaval.
| Subject | Soil Mechanics |
| Unit | Soil Formation & Properties of Soil |
| Topic | Formation of Soil |
| Next Topic | Types of Soil |
| Previous Topic |