Soil water & Types of soil
Water present in the soil in any form is termed soil water. Many types of sοil water.
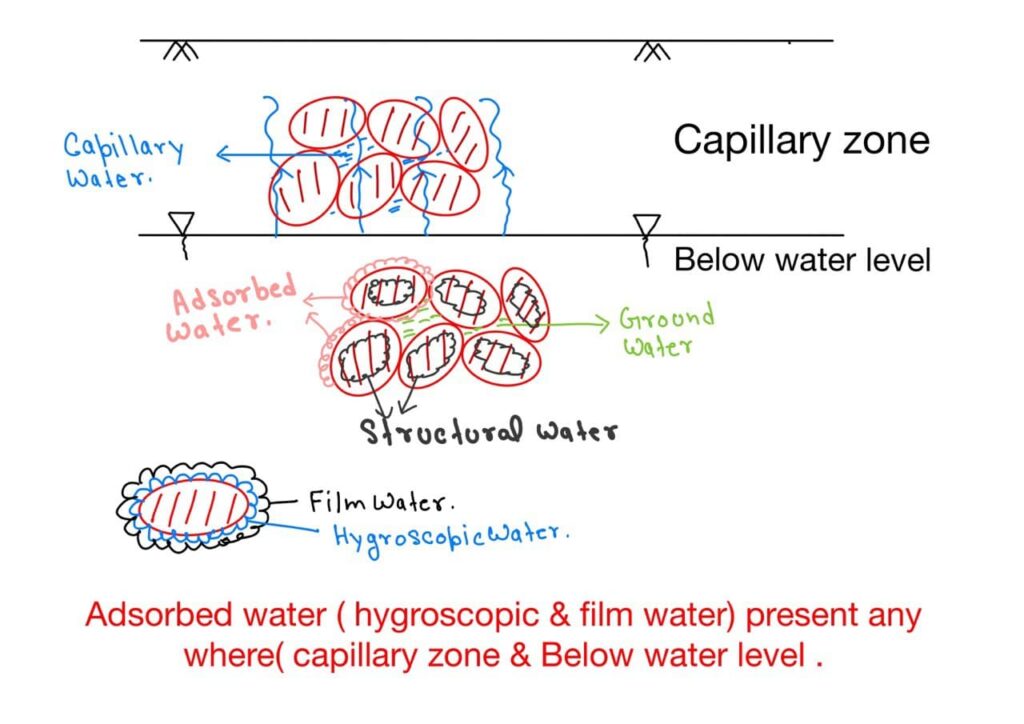
- Ground / Free / Gravity water
- Capillary water
- Structural water
- Adsorbed water
Ground / Free / Gravity water:
- It is subsurface water that fills the voids continuously up to groundwater table level ( So is called ground water ) .
- This water is subjected to no force ( So is called free water ) other than its own weight ( So is called gravity water ) .
- It obeys all the laws of hydraulics and is capable of moving under hydrodynamic force.
Capillary water:
- It’s the water which is lifted above ground water table level by capillary force.
- It remained in suspension in the voids of soil.
- It also obeys laws of hydraulic and moves under hydrodynamic force.
Note: Groundwater and capillary water are also terms as pore water.
Structural water
- It is the water which is chemically combined with crystal structure of the soil.
- Under loading conditions observed in engineering, structural water cannot be removed even by increased temperature at 105 to 110 degree.
Adsorbed water / Pellicular water
- Hygroscopic water
- Film water
Hygroscopic water
- It is the water which is adsorbed by soil solids from the atmosphere by physical force of attraction and is held over its surface due to adhesion.
- The extent of water adsorbed by the soil solid ∝ ( 1/size .d) ∝ surface area.
- Hygroscopic water is not affected by Gravity or capillary forces.
- It has higher density, viscosity & boiling point and lesser freezing point than groundwater.
- The hygroscopic adsorption capacity of different soil.
- The water adsorption capacity for clay⇒ 16 – 17 %.
- The water adsorption capacity for silt⇒ 6 – 7 %.
- The water adsorption capacity for Sand⇒ 1-2 %.
Film water
- It is the water that is present as a film over the layer of hygroscopic water.
- It is formed due to the condensation of aqueous vapor.
- It is also held by soil solids but has lesser adhesion than hygroscopic water.
Hygroscopic water & Film water not followed the law of Hydrodynamics.
 Soil Water & Types of Soil Water
Soil Water & Types of Soil Water
| Subject | Soil Mechanics |
| Unit | Soil Formation & Properties of Soil |
| Topic | Soil Water & Types of Soil Water |
| Next Topic | Void Ratio and Porosity of Soil |
| Previous Topic | Water Content or Moisture Content |