Determination of Water Content of Soil
The various techniques for determining the water content of soil are as follows:
- Oven Drying Method
- Sand Bath Method
- Alcohol Method
- Pycnometer Method
- Calcium Carbide or Moisture Meter Method
- Radiation Method
- Torsional Balance Method
Oven Drying Method
- This is the most accurate laboratory method.
- In this method moist sample of soil is placed in a dry container of mass M1 & its total mass is noted M2.
- The moist sample along with the container is placed in temperature controlled oven for drying.
- For inorganic soil temperature is maintained in 105ºC to 110ºC range.
- For Organic soil temperature is maintained at less than 60ºC degrees (To avoid oxidation of organic matter).
- For soil having high gypsum (CaSo4.2H20) content temperature is kept to less than 80ºC ( To avoid loss of water of Crystallization).
- For sand & gravel drying is regular for 4-6 hours, for clay & silt drying is regular for 16-20 hours. However, drying is for 24 hours to ensure a complete loss of water.
- In no case, the temperature should exceed 110ºC as it would lead to loss of structural water.
- In this method, all types of soil water are removed ( Ground, Capillary, Adsorbed, except structural water.)
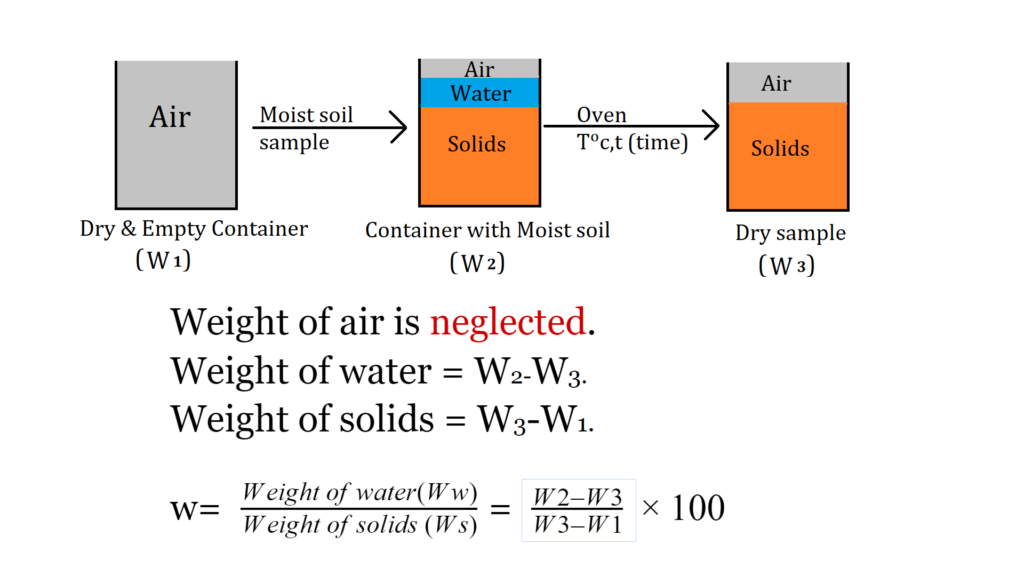
Oven Dry Method
W1= Weight of empty container.
W2= Weight of container+ moist sample soil.
W3= Weight of container +dry sample.
Sand Bath Method
- It is a quick field method that is used when the facility of the electric oven is not available.
- In this method, a moist sample of soil along with the container (Weight W2) is placed in a sand bath and is heated over Kerosene Stove, after heated weight of the dry sample with the container is W3.
- As there is no control over the temperature in this case it is not suitable for high organic soil & soil having high gypsum content moreover, it gives inaccurate results due to loss of structural water.
- Steps of observation are same as oven drying method.
W1= Weight of empty container.
W2= Weight of container+ moist sample soil.
W3= Weight of container +dry sample.
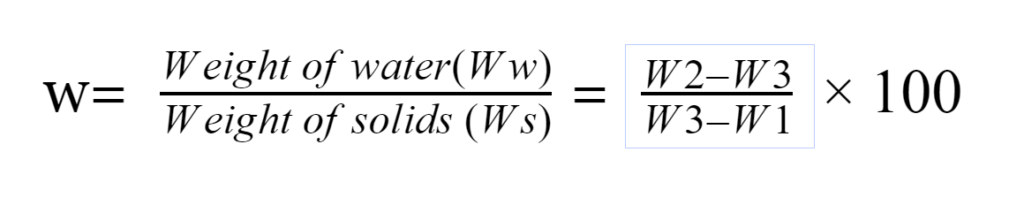
Alcohol Method
- It is also a quick field method.
- In this method methylated Spirit (ALCOHOL) is added to the sample ( it increases the rate of drying ) & ignited to note the water content.
- Here also there is no control over temperature hence it is not suitable for Organic soil or soil having high gypsum content, moreover it gives inaccurate results due to loss of structural water.
- The Series of observations is the same as oven drying.
Pycnometer Method
- It is a quick field method that gives the result in 10 to 20 minutes.
- This is suitable for those soil whose Specific Gravity ‘G’ is known.
- This method is used for cohesionless soils in the case of cohesive soil it is very difficult to remove entrapped air from soils sample during the test.
- The Pycnometer is a 900ml flask having a conical top with a 6mm diameter circular hole at the top to remove air from the sample.
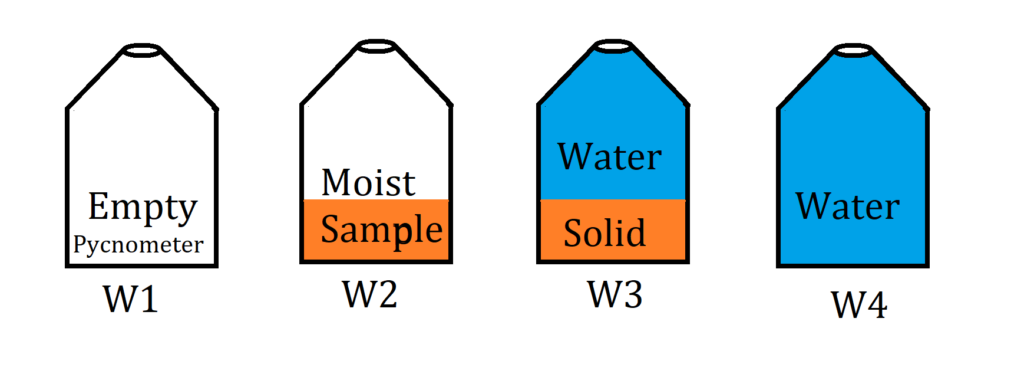
PycnometerW1=Weight of empty pycnometer.
W2= Weight of pycnometer + Moist soil.
Moist Soil =( Solid+ Water + Air)
W3= Weight of pycnometer + Moist soil + water.
W4= Weight of pycnometer + water.
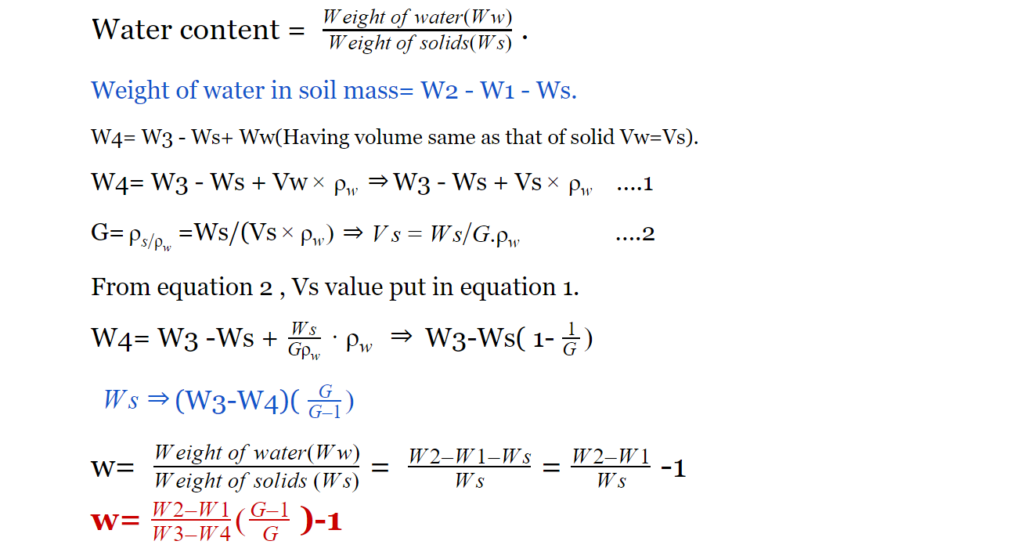
Calcium Carbide or Moisture Meter Method
- It is one of the quickest methods available to find water content which gives the result in 5-7 minutes.
- It is a field method.
- In this method, 4-6 (5) gram of soil sample (fixed weight is taken due to calibration) which is then placed in moisture matter and calcium carbide (CaC2) is added & sample is shaken continuously, due to which calcium carbide reacts with water present in it & result in the formation of Acetylene gas (C2H2) that exerts the pressure on calibrated gauge to report water content in terms of the total weight of soil (w’)
CaC2 +2H20 → C2H2↑ + Ca(OH)2
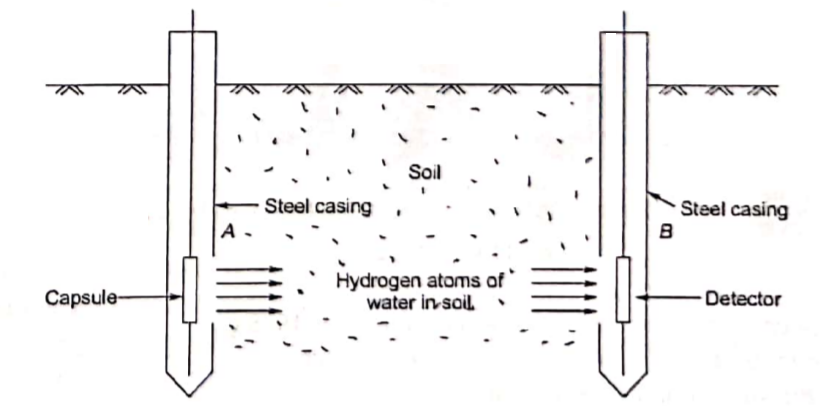
Radiation Method
- It is a field method in which two Steel casings are lowered into the soil mass to be tested.
- In the first casing, a radioactive material (CO-60) is placed & in another casing detector is placed.
- When radioactive materials are activated it emits neutron which when struck is a Hydrogen atom of water that loses its energy is further detected by a detector & is calibrated with the water content of the soil.
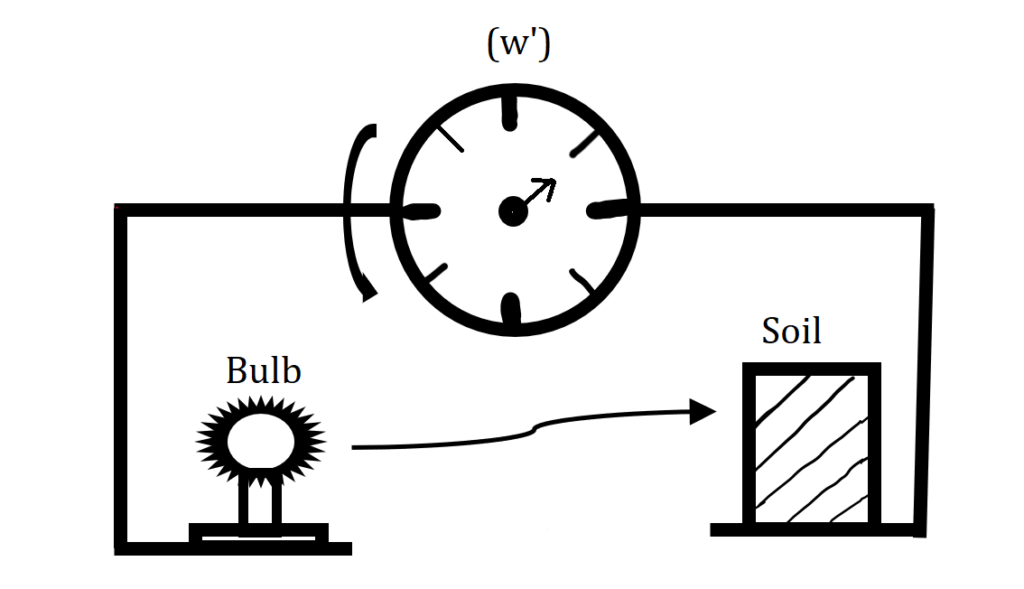
Torsional Balance Method
- In this method, infrared rays are used for drying of the soil sample.
- This method is suitable for those soil which is absorbed the moisture from the atmosphere as in this case drying & weighing of the sample is done simultaneously.
- Infrared rays are generated by 250watt , 230volt , 50Hz ,frequency bulb.
- Here also water content of the soil in terms of total weight of soil is measured (w’).
| Subject | Soil Mechanics |
| Unit | Soil Formation & Properties of Soil |
| Topic | Determination of Water Content of Soil |
| Next Topic | Soil Water & Types of Soil Water |
| Previous Topic | Water Content or Moisture Content |