Test of Specific Gravity
- The specific gravity of soil can be computed using a 50 ml density bottle, 500 ml flask, or by pycnometer.
- The density bottle method is the most accurate among all & is suitable for all types of soil.
- Flask & Pycnometer is suitable to be used for coarse-grained soil & If it is used for fine-grained soil then kerosene is used in the test instead of water ( as kerosene is a better wetting reagent than water)
- In the density bottle, only kerosene is used.
- Steps of observation in all same.
Density bottle⇒all types of soil ⇒ only kerosene used.
Flask & Pycnometer
- Coarse-Grained soil ⇒ Water /Kerosene.
- Fine-Grained soil ⇒Only Kerosene Used.
The process of determining specific gravity are same for a 50 ml density bottle, 500 ml flask, or Pycnometer. Here we use a pycnometer.
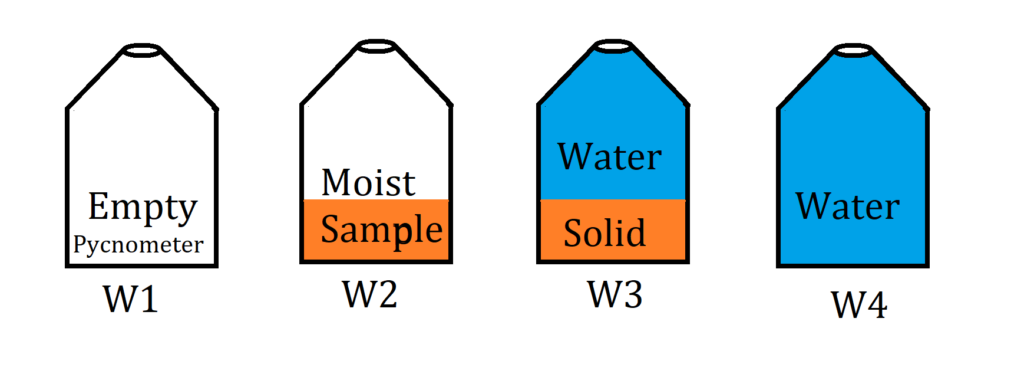
W1=Weight of the empty pycnometer.
W2= Weight of pycnometer + Dry soil.
W3= Weight of pycnometer + Dry soil + water.
W4= Weight of pycnometer + water.
\(\mathrm{G} / \mathrm{GS}=\frac{\text { Weight of solid of given soil }}{\text { weight of standard fluid of same volume }}\)
Standard Fluid=Water
\(G=\frac{Ws}{Ww orWk}\) \(G=\frac{ρ_s}{ρ_w or ρ_k}\) \(G=\frac{Ms}{Mw or Mk}\)Mass of solids Ms = M1-M2 =Mass of dry soil =Md
Mass of water in stage 3 = M3-M2
Mass of water in stage 4 = M4-M1
(Mass of water having volume same as that of solids= Mass of water in stage 4 -Mass of water in stage in stage 3)
Mass of water having volume same as that of solids= (M4-M1)-(M3-M2)
=M4-M3+M2-M1
=M4-M3+Md
Or M4+M3-Md+Mw(whose volume is the same as that of solids )
Mw=M4-M3+Md
\(G=\frac{M2-M1}{M4-M3+M2-M1}\)\(G=\frac{Md}{M4-M3+Md}\) ***
G = Specific Gravity of solid.
Note: Kerosene is used instead of water for fine-grained soil. Then Specific Gravity is calculated as
\(G=\frac{M2-M1}{M4-M3+M2-M1}×Gk\) ***
Gk = Specific Gravity of Kerosene.
| Subject | Soil Mechanics |
| Unit | Soil Formation & Properties of Soil |
| Topic | Test of Specific Gravity |
| Next Topic | Test of Unit Weight of Soil |
| Previous Topic | Interrelationship Between the Properties of Soil |