Divider /Medians / Traffic separators
- Divider is an element provided to Road along the center line to separate two way traffic. The main function of median is to prevent “Head on collision” between vehicles moving in the opposite direction. it also serves following other functions:
- To channelize traffic into the streams.
- To protect the pedestrians.
- Glaring effect due to Head light of the opposite direction vehicle can be reduced.
- To segregate the slow traffic.
- Medians can be provided in following forms:
- As pavement marking
- Physical dividers (Mechanical separator)

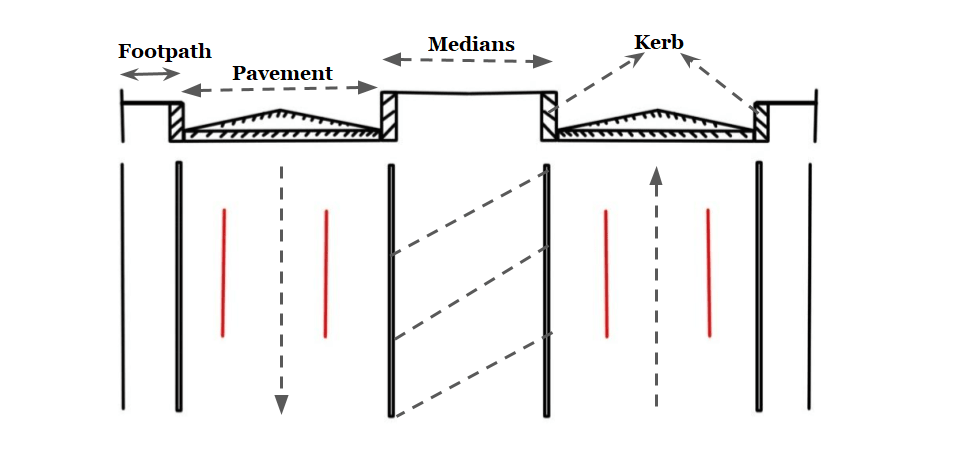
- Desirable width of median is 8- 14 meter. ( It includes the provision for future expansion of roads)
- In order to reduce the glare of head light of opposites moving vehicle minimum width is required is 6 meter.
- IRC recommended minimum width of 5 meter for divider than can be reduced to 3 meter where land in restricted.
- On the bridges width required for median is in the range of 1.2 to 1.5 meter.
- In urban area minimum width of median to be provided is 1.2 meter & desirable min is 1.5 meter.
- For Expressway min width to be provided is 12 meter and desirable is 15.5 meter.
Note: This topic is part of the second chapter of Highway Engineering. I suggest reading this topic in the context of the complete chapter: Geometric Design of Highway. If you want to read the entire Highway Engineering, click here: Highway Engineering.
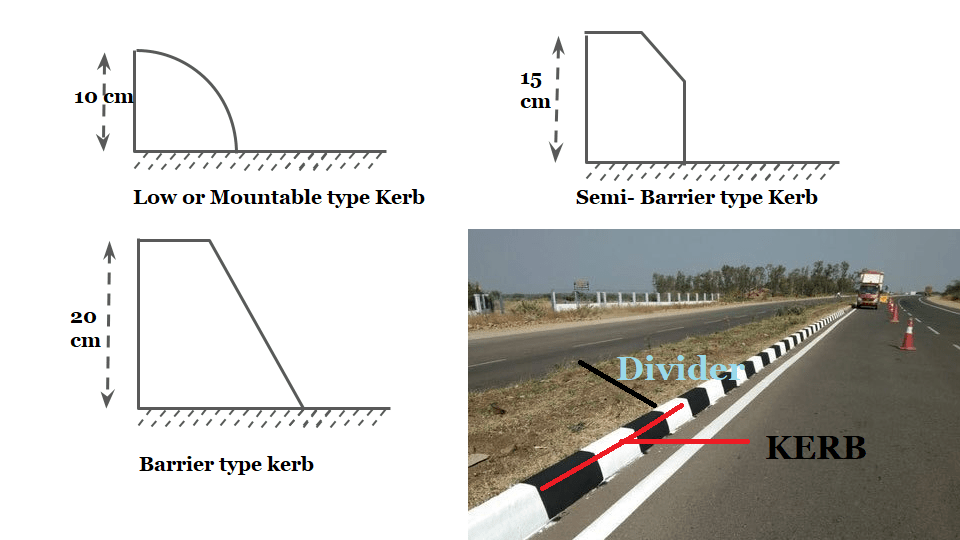
Kerb
- Low or Mountable type Kerb
- Semi- Barrier type Kerb
- Barrier type kerb
- Kerb is a separator between pavement & footpath. It provided lateral support to the pavement.
- Kerb are mainly divided into following 3-categories.
1.Low or Mountable type Kerb:
Height of this type of kerb is about 10 cm with a slope or batter to help the vehicle climb the kerb easily.
2.Semi- Barrier type Kerb:
Height of this type of Kerb is about 15 cm with a batter of 1:1 on the top 7.5 cm. It is provided where pedestrian traffic is high.( Pedestrian = A person who is walking in the street.)
3.Barrier type kerb:
Height of kerb stone is about 20 cm with a batter of 1:4.
Function of kerb are:
- To facilitate and control drainage.
- To delineate the pavement edge.
- To present a more finished appearance.
- To strengthen and produce the pavement edge.
For Detailed Analysis of Highway Engineering Step By Step.