Curve:
Curves are provided in highways in order that the change of direction at the intersection of straight alignments either in horizontal or vertical plane, shall be gradual.
Note: This topic is part of the second chapter of Highway Engineering. I suggest reading this topic in the context of the complete chapter: Geometric Design of Highway. If you want to read the entire Highway Engineering, click here: Highway Engineering.
The necessity of curves arises due to the following reasons:
- Topography of the country
- To provide access to a particular locality
- Restrictions imposed by property
- Preservation of existing amenities
- Avoidance of existing religious, monumental and other costly structures
- Making use of existing right of way
Advantages of Curves
The advantages of providing curves are:
- They provide comfort to the passengers. If there is an abrupt change in the direction nor grade of a highway it will upset the passengers.
- They help to avoid mental strain induced by the monotony of continuous journey along straight path.
- In the case of sharp turns, brakes have to be applied more frequently which reduces the life of tyres. Thus life of the vehicles in increased by providing curves.
- The drivers became alert due to the change in the direction of road.
- They help to keep the speed of the vehicle within limits. On a straight road, a driver is tempted to go at a much faster speed.
Factor Affecting the Design of Curves
The various factors which affect the design of curves are:
- Design speed of the vehicle
- Maximum permissible superelevation
- Allowable friction
- Permissible centrifugal ratio
Type of Curves
Curves have been divided into two classes:
(1) Horizontal Curve: A curve in plan to provide change in direction of the central line of a road.
(ii) Vertical Curve: A curve in the longitudinal section of a roadway to provide for easy change of gradient.

The different types of curves used in highways are:
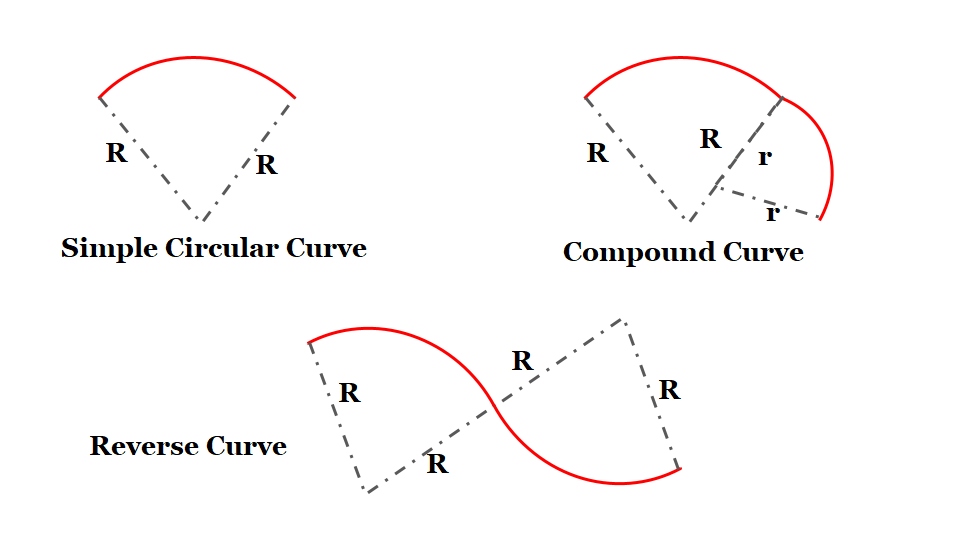
(i) Simple Circular Curve: A simple cùrve consists of a single are connecting two straights.
(ii) Compound Curve: A compound cùrve consists of a series of two or more simple curves that turn in the same direction and join at common tangent points.
(iii) Reverse Curve: A reverse cúrve consists of two simple curves of opposite direction that join at the common tangent point called the point of reverse curve.