Camber / Cross- Slope:
Note: This topic is part of the second chapter of Highway Engineering. I suggest reading this topic in the context of the complete chapter: Geometric Design of Highway. If you want to read the entire Highway Engineering, click here: Highway Engineering.
- It is the slope provide to the road surface in the transverse direction to drain the rainwater from the road surface to avoid the following:
- Stripping of bitumen from the aggregate in the presence of the water.
- In order to avoid swelling of sub grade in case water seeps up to it.
- The slipping of the vehicle over the wet pavement.
- Glare over the wet pavement surface.
- On straight Road it is provide by raising the center of carriage way with respect to edges forming the crown on the highest point along the center line.
- At horizontal curve with super elevation, the surface drainage is provided by raising the outer edge.
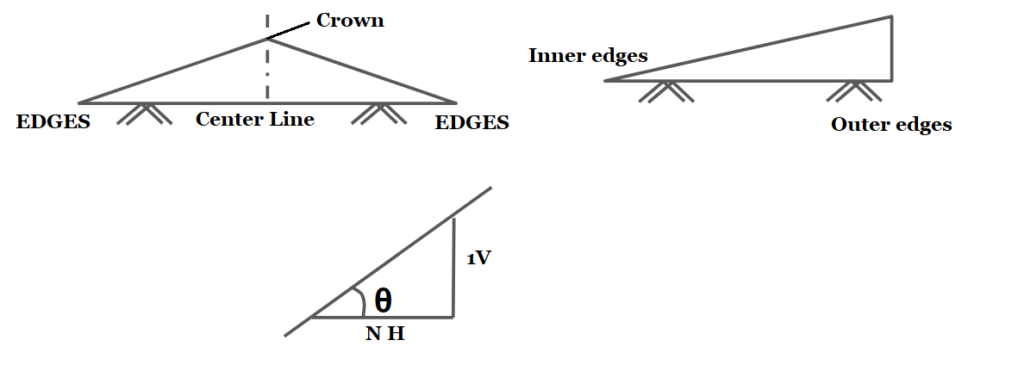
- It is represented in any of the following ways:
- As percentage :For example cross-section 5% ⇒ tanθ = \(\frac{5}{100}\).
- As fraction : For example cross- section = 1 in 20 = \(\frac{1}{20}\) = 0.05.
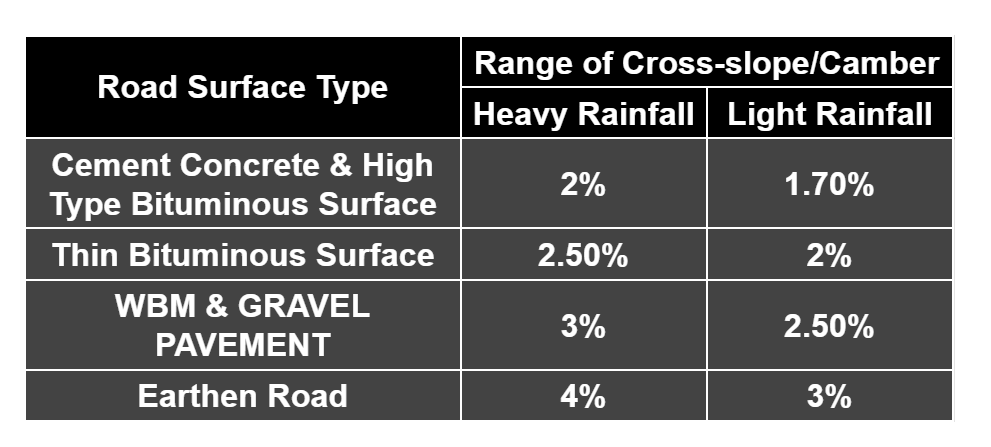
- The value of cross-section depend on following factor:
- Type a pavement surface
- Amount of rainfall
Type of Cross- Slope / Camber
Straight line Cαmber
Parabolic Cαmber
Composite Cαmber
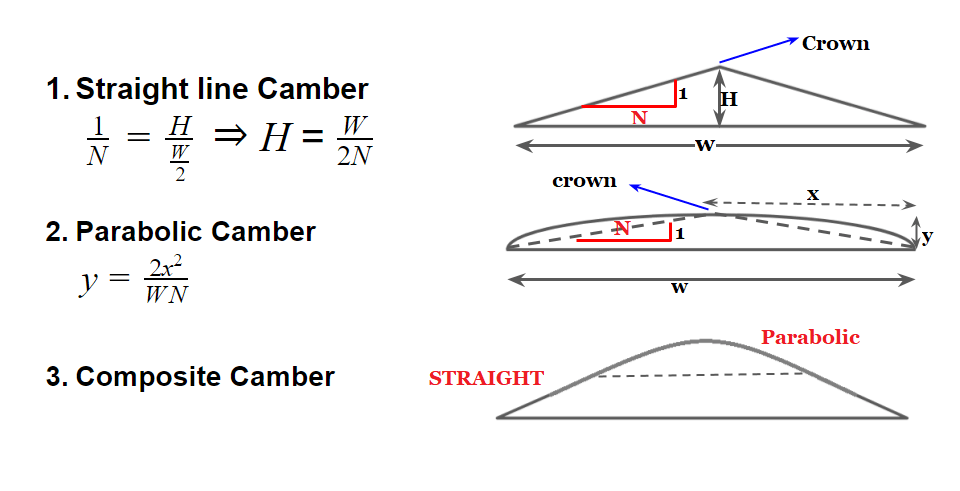
Note: For cement concrete pavement straight line camber is preferred. As it is easier to lay.
Gradient = 2x Cαmber
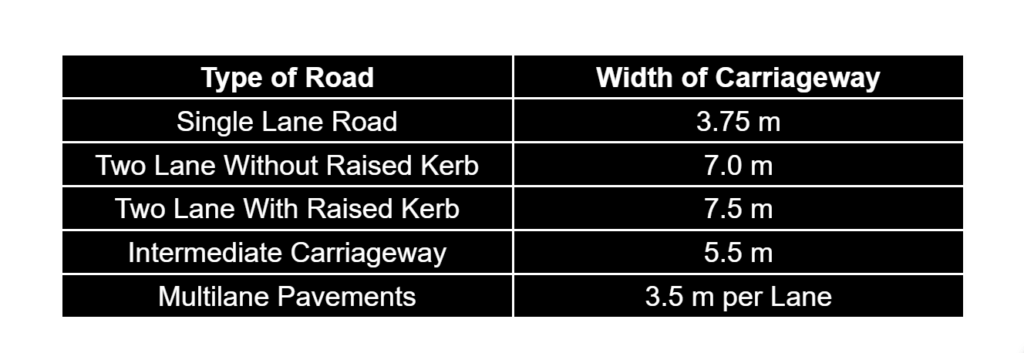
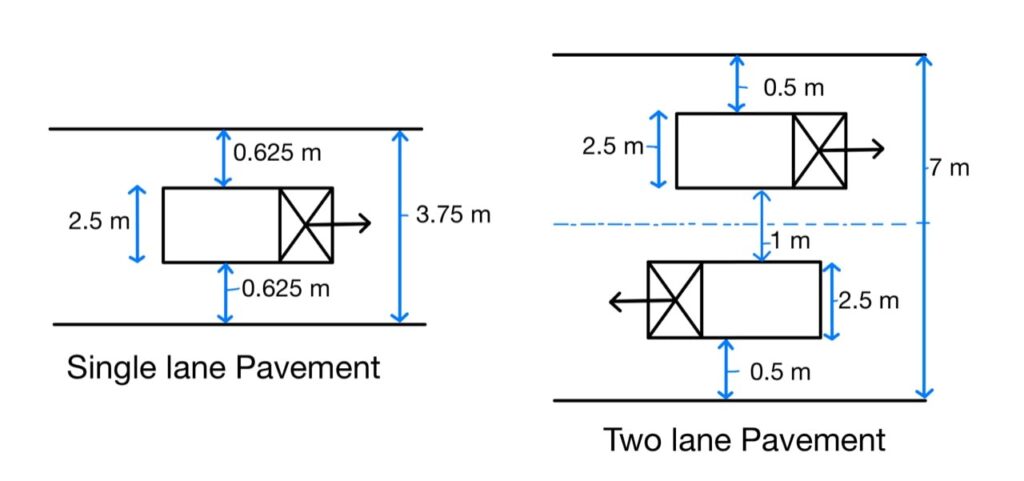
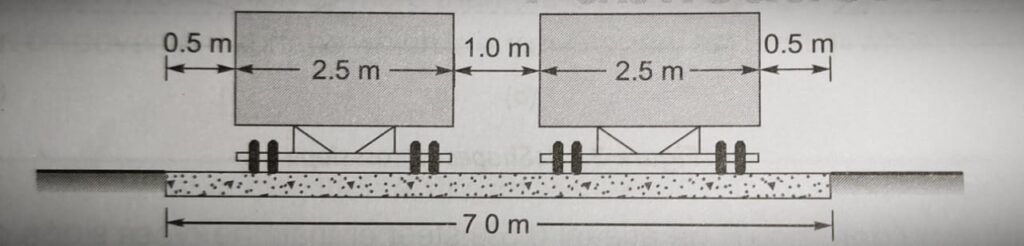
Width of Pavement or Carriageway:
- Width of payment depends upon width of traffic, lane and number of lanes.
- Width of traffic lane is decided on the basic the type of vehicle moving on it, along with same clearance in both the sides.
- Passenger car is considered as a standard vehicle to decide the width of carriageways. (Width of passenger car = 2.44 meter= 2.5 meter)
- For rural highway, if pavement has two or more lane, width of single lane is 3.5 meter.
- The number of lane to be provided depends upon traffic volume.
- The width of carriageway for different conditions are follow.
For Detailed Analysis of Highway Engineering Step By Step.