Void Ratio
It is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids (Vv) to the volume of solids(Vs) present in a given soil mass. It is represented as ‘e’.
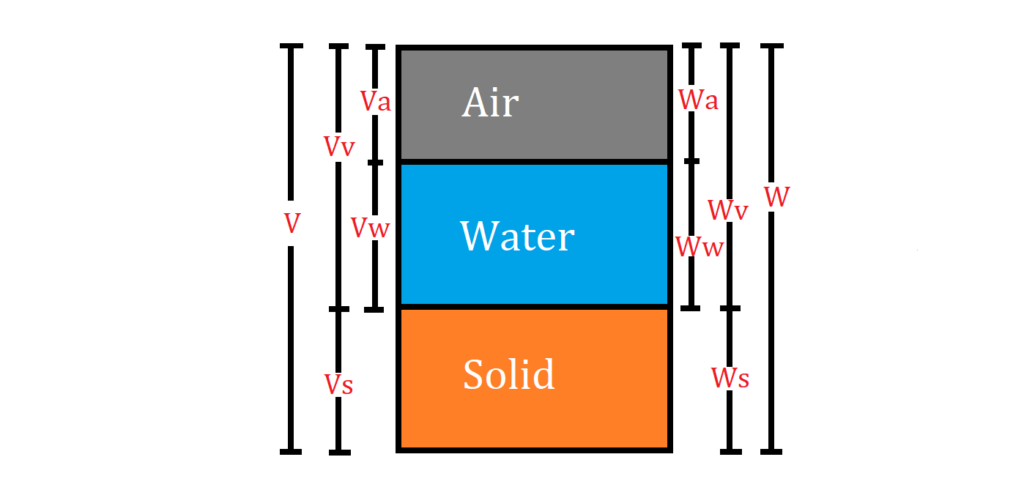
Voids Ratio (e) = Volume of voids (Vv) / Volume of solids (Vs).
Voids Ratio is the Unit less.
Voids Ratio (e) >0.
\(e_{\min }\)=0.91.
⇒Volume of the void cannot be zero for soil as it is at least a two-phase system, however it can be zero for rock.
e = Vv / Vs . Add 1 on both sides.
e+1 = Vv/Vs +1.
e+1 = (Vv+Vs)/Vs. We know that Vv+Vs= V (total volume of soil).
e+1 =V/Vs
Vs= V / (e+1)
⇒Void ratio can also be used to represent the degree of denseness of soil. (Denseness: Degree of packing.)
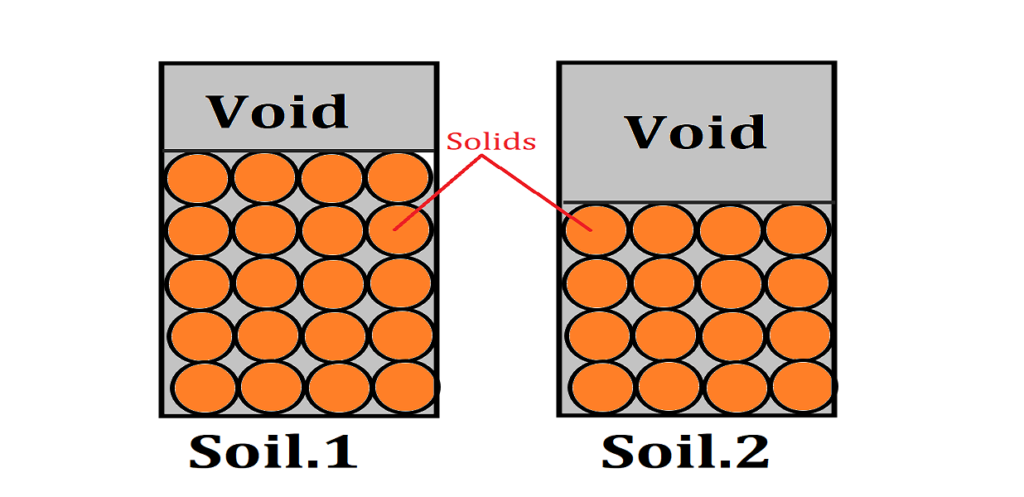
V1 = V2 V= Total volume of soil
e2 > e1.
Vv2 > Vv1.
Vs2 < Vs1.
(Denseness)2 < (Denseness)1.
Denseness ∝ 1/e.
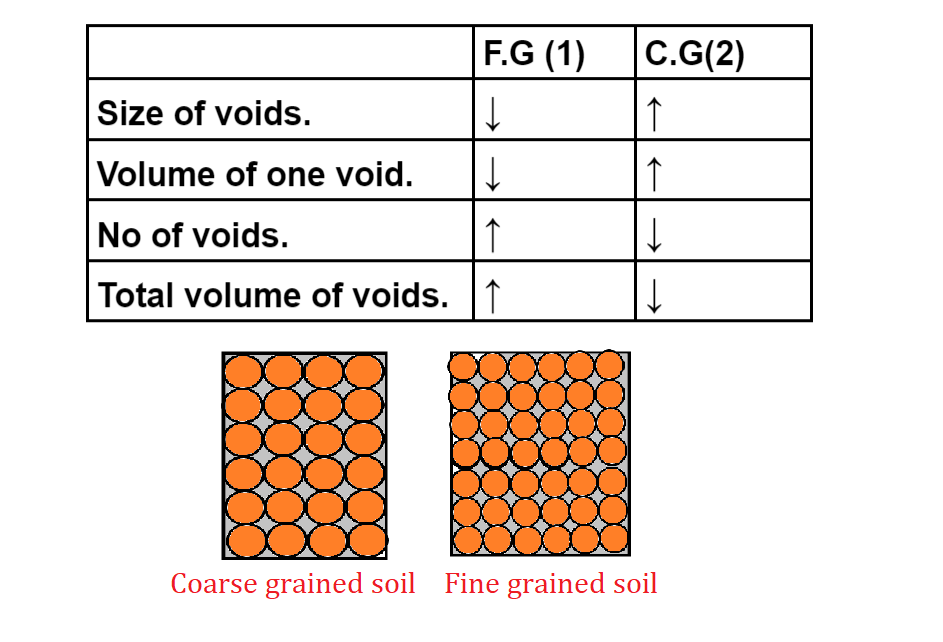
⇒ Though the volume of one void is more for a coarse-grained but total volume of voids is more for fine-grained soil, hence void ratio & water content of fine-grained soil is more than coarse-grained soil. ( For comparison make sure the volume of fine-grained soil & volume of coarse-grained soil are the same.)
⇒ Whenever two or more soil samples are mixed, the quantity ( volume& weight ) of solids will not change.
If , Soil (A) +Soil (B) = Soil (C).
- Vs(A) + Vs (B) = Vs (C).
- Ws(A) +Ws(B) = Ws(C).
⇒ Quantity of solid remains the same If soil is displaced from one to another location.
Porosity (η)
It is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids(Vv) to the volume of soil (V) present in the given soil mass. It is represented as ‘η’.

η= Vv / V *100
Porosity is the Unit less.
0% < η < 100%.
η = Vv / V
η = Vv/ (Vv+Vs) = (Vv/Vv)/{(Vv/Vv)+(Vs/Vv)}.
η = 1/(1+1/e).
η = e / (1+e).
or e = η / (1-η).
⇒ Both e & Significant the water storage capacity of soil as they represent volume of voids in it.
⇒Volume of solid is comparatively stable in comparison to volume of soil as it does not change with change in volume of voids , hence engineering significance of e>η .
NOTE:
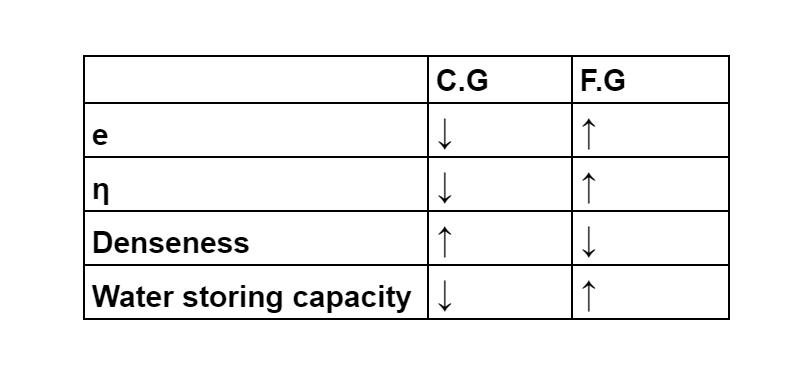
- With increasing Void ratio & Porosity, water storing capacity is increased.
- Voids Ratio of Coarse-grained soil is less and fine-grained soil is more of the same volume of soil.
- Porosity of Coarse-grained soil is less and fine-grained soil is more of the same volume of soil.
- The denseness of Coarse-grained soil is more and fine-grained soil is less of the same volume of soil.
- The water storing capacity of Coarse-grained soil is more and fine-grained soil is less of the same volume of soil.