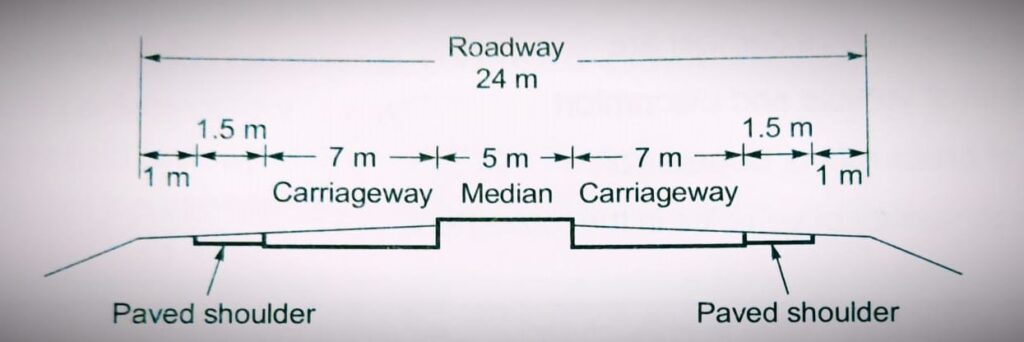
Shoulder:
- Extra width provided adjacent to edge of pavement is called shoulder. It is provided for emergency point of view like Breakdown of vehicle, medical emergency etc.
Note: This topic is part of the second chapter of Highway Engineering. I suggest reading this topic in the context of the complete chapter: Geometric Design of Highway. If you want to read the entire Highway Engineering, click here: Highway Engineering.
As per IRC
- Minimum width of shoulder required for a highway is 2.5 meter.
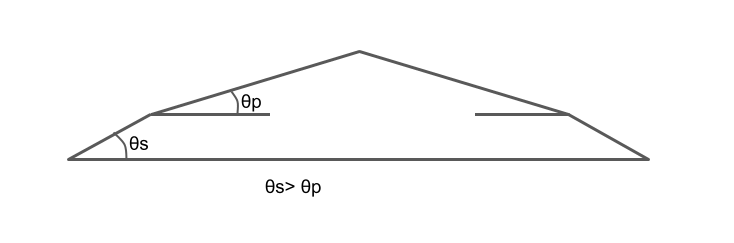
- Cross slope of shoulder should be 0.5% more than cross slope of adjoining pavement, having minimum value of 3% & maximum value of 5%.
- 5% ⊀ cross slope(shoulder)= (0.5%+ cs of pavement) ⊀3%.

Slope of Shoulder
Road Margin:
These are the areas which are not used as regular roadways. The various elements include in the road margins are as follows:
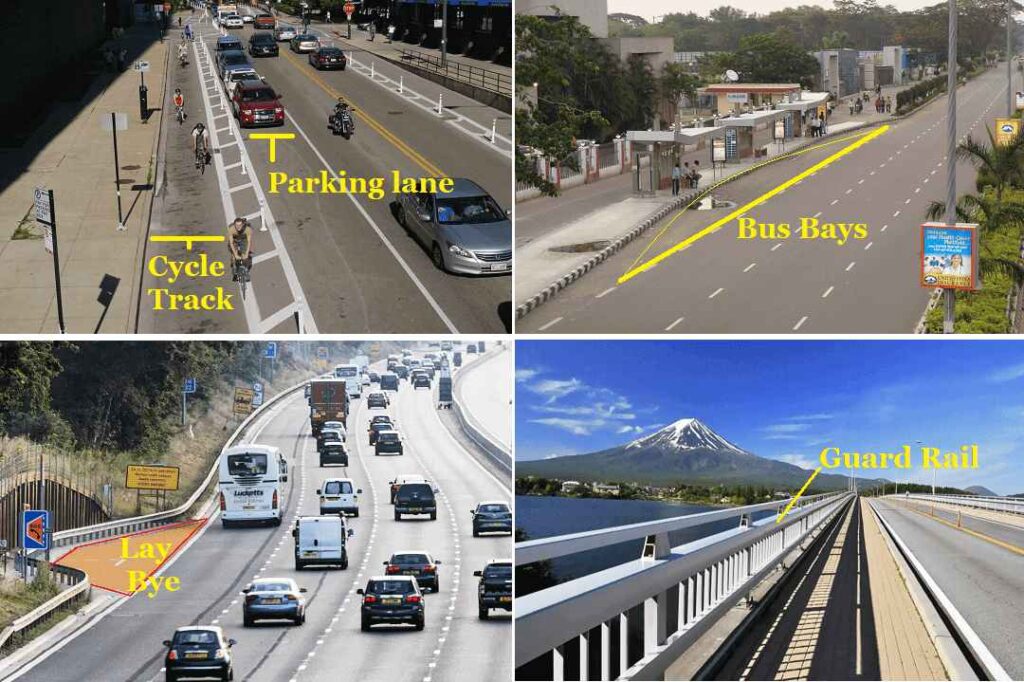
- Parking lane: These are generally provided on an urban road to allow car parking. Parallel parking is generally provided for safe moving of vehicles. However angle parking is also provided. Parking lane should have sufficient width. For parallel parking 3.0 m width is required.
- Lay Bye: These are provided near public convenience to avoid the conflict with a running traffic minimum width is 3 meter.
- Cycle Track: These are provided in urban areas for the safe movement of cycle traffic. The minimum width required is 2 meter for the cycle track and it can be increased by 1 m for each additional cycle lane.
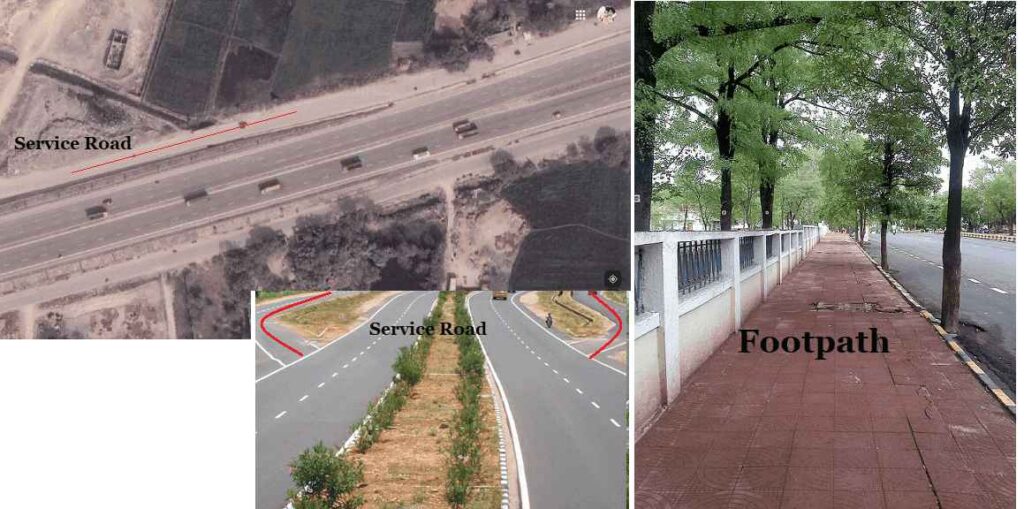
- Drive way: these are used to connect the highway with commercial establishments like fuel stations, service-station etc.
- Footpath: These are providing urban roads having heavy vehicular as well as pedestrian traffic, to provide the protection to pedestrians. Minimum width of footpath should be 1.5 m and it may increase based on the pedestrian traffic volume.
- Guard Rail: These are provided at the edge of shoulder when the road conditions on fill to prevent vehicles from running off the embankment. Guard stones are installed at a suitable distance to provide better night visibility on the curves under headlights of the vehicle.
- Service Road: These are provided parallel to the highway and isolated by a separator and access to highways provided only at selected points. They are provided to avoid congestion on the highway and expressway.
- Bus Bays: It may be provide by recessing the kerb to avoid the conflict with the moving traffic and must be located at least 75m away from the intersection. It is used for safe plying of Passenger and Cargo from Bus.

For Detailed Analysis of Highway Engineering Step By Step.